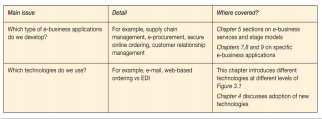
- Outline the hardware and software technologies used to build an e-business infrastructure within an organization and with its partners
- Outline the hardware and software requirements necessary to enable employee access to the Internet and hosting of e-commerce services.
TYPICAL PROBLEMS
- Web site communications too slow.
- Web site not available.
- Bugs on site through pages being unavailable or information typed in forms notbeing executed.
- Ordered products not delivered on time.
- E-mails not replied to.
- Customers’ privacy or trust is broken through security problems such as creditcards being stolen or addresses sold to other companies.
E-BUSINESS INFRASTRUCTURE
The architecture of hardware, software, content and data used to deliver e-business services to employees, customers and partners.
KEY MANAGEMENT ISSUES OF E-BUSINESS INFRASTRUCTURE
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGIES USED TO BUILD AN E-BUSINESS
WHAT IS THE INTERNET ?
“The Internet, sometimes called simply "the Net," is a worldwide system of computer networks - a network of networks in which users at any one computer can, if they have permission, get information from any other
computer” -whatis.com “A global network connecting millions of computers. More than 100
countries are linked into exchanges of data, news and opinions. -webopedia.com “is logically linked together by a globally unique address space based on the Internet Protocol (IP) or its subsequent extensions/follow-ons”-FNC
อินเทอร์เน็ต .......... ?
-อินเทอร์เน็ต (อังกฤษ: Internet) หมายถึง เครือข่ายคอมพิวเตอร์ขนาดใหญ่ ที่มีการ
เชื่อมต่อระหว่างเครือข่ายหลาย ๆ เครือข่ายทั่วโลก โดยใช้ภาษาที่ใช้สื่อสารกันระหว่าง
คอมพิวเตอร์ที่เรียกว่า โพรโทคอล (protocol) ผู้ใช้เครือข่ายนี้สามารถสื่อสารถึงกันได้
ในหลาย ๆ ทาง อาทิ อีเมล เว็บบอร์ด และสามารถสืบค้นข้อมูลและข่าวสารต่าง ๆ
รวมทั้งคัดลอกแฟ้มข้อมูลและโปรแกรมมาใช้ได้
HOW BIG IS THE INTERNET?
-Over 1 billion Internet users worldwide
-How big the infrastructure they accessing?
-Measured by number of servers
-Number of pages indexed by search engines
INTERNET USERS PER 100 INHABITANTS
Source: "Internet users per 100 inhabitants 2006-2013", International Telecommunications Union, Geneva, accessed 3 June 2013
INTERNET USERS BY LANGUAGE
Source: "Number of Internet Users by Language", Internet World Stats, Miniwatts Marketing Group, 31 May 2011. Retrieved 22 April 2012
WEBSITE CONTENT LANGUAGES
Source: "Usage of content languages for websites". W3Techs.com. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
THE NETCRAFT INDEX OF NUMBER OF SERVERS
Source: Netcraft Web Server Survey. http://news.netcraft.com/archives/web server survey.html. Netcraft, http://netcraft.com
Intranet : A private network within a single company using Internet standards to enable employees to share information
Extranet : Formed by extending an intranet beyond a company to customers, suppliers and collaborators
INTRANET AND EXTRANETTHE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTRANETS, EXTRANETS AND THE INTERNETINTRANET AND EXTRANET
Intranet applications
- Used extensively for supporting sell-side e-commerce
- Also used for internal marketing communications
Extranet applications
- Used to provide online services which are restricted to business
customers
BUSINESS BENEFITS OF EXTRANET
-Information sharing
-Cost reduction
-Order processing and distribution
-Customer service
PREMIER DELL.
COMQUESTIONS ON EXTRANET?
-Are the levels of usage sufficient?
-Is it effective and efficient?
-Who has ownership of the extranet?
-What are the levels of service quality?
-Is the quality of information adequate?FIREWALLS
-A specialized software mounted on a separate server at the point where the company is connected to the Internet
-Use to protect information on the company
FIREWALLS
Firewall positions within the e-business infrastructure of the B2B company
INFORMATION EXCHANGE BETWEEN A WEB BROWSER AND WEB SERVER
WEB EVOLUTIONWEB
INTERNET TOOLS
- Instant messaging (IM) and Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
- Usenet newsgroups
- FTP file transfer
- Telnet
- Blogs
- RSS (Really Simple Syndication)
- World Wide Web
- IPTV
- BitTorrent
MANAGING E-BUSINESS INFRASTRUCTURE
- Layer II – Systems software
Standardization throughout
organization
- Layer III – Transport or network
Based on internal company network
- Laver IV – Storage
Based on company needs
DIFFERING USE OF APPLICATIONS AT LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT WITHIN COMPANIES
NEW ACCESS DEVICES
- Mobile access devices
- Wi-Fi mobile access
- Bluetooth
- Next-generation mobile services
- Interactive digital television
Mr. Chayaphat Phumchun
Business Computer Department Chiangmai Rajabhat University
Business Computer Department Chiangmai Rajabhat University


















ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น